If your job posting never gets in front of the right eyes, are you even hiring?
How did you write the job description for the last role you posted? If the title sounded anything like “Growth Ninja,” “Technology Evangelist,” or “Sales Superstar,” we need to talk. Because while it might feel like you are standing out in a sea of job openings, you are actually tanking the visibility of your posting.
The truth: the way candidates discover jobs has fundamentally changed as search has evolved.
The mismatch: the way many HR leaders write job descriptions has not. Or worse, they are letting AI do the driving when AI should be riding shotgun (that’s a blog post for another day, though).
I am a Senior Growth Marketer at The Predictive Index, and there are two things you should know about me.
- I spend my Monday through Friday deep in the pain points of HR leaders. You all are heroes.
- I live and breathe growth marketing, and the way search has evolved over the last three years is hard enough for even the best SEO experts to keep up with.
So I am here, as a growth marketer in a never-ending fight with Google, doing my best out here to share my no-BS tips for getting your job descriptions found in search.

How Job Discovery Actually Works Now (Search, Social, AI)
If your job description cannot be interpreted by machines, it will not get surfaced. Full stop. It doesn’t matter how compelling the role is.
That is the reality of modern job discovery. Candidates no longer rely solely on recruiters, job boards, or alerts. Jobs are found, filtered, and excluded by systems long before a human ever sees them.
When you think about where your job posting can be discovered, there are three places that actually matter:
- Search engines
- LinkedIn and job platforms
- AI Chat Bots (LLMs, and yes, this is new, and yes, it already counts)
Each of these channels behaves differently. Your job description needs to work in all of them.
How can I optimize job descriptions for Search Engines (Google, Bing)?
Search engines like Google and Bing are often the first stop for candidates. Roughly 70 percent of job seekers use Google at some point in their search.

In competitive markets, especially those flooded with AI-generated applications, strong candidates do not wait for recruiters to land in their inbox. They go looking. And like any good candidate you’d want to hire, they are getting smarter about how they do it.
Many candidates still use Boolean searches in Google. What’s a Boolean search?
This looks like typing something like the following into Google search:
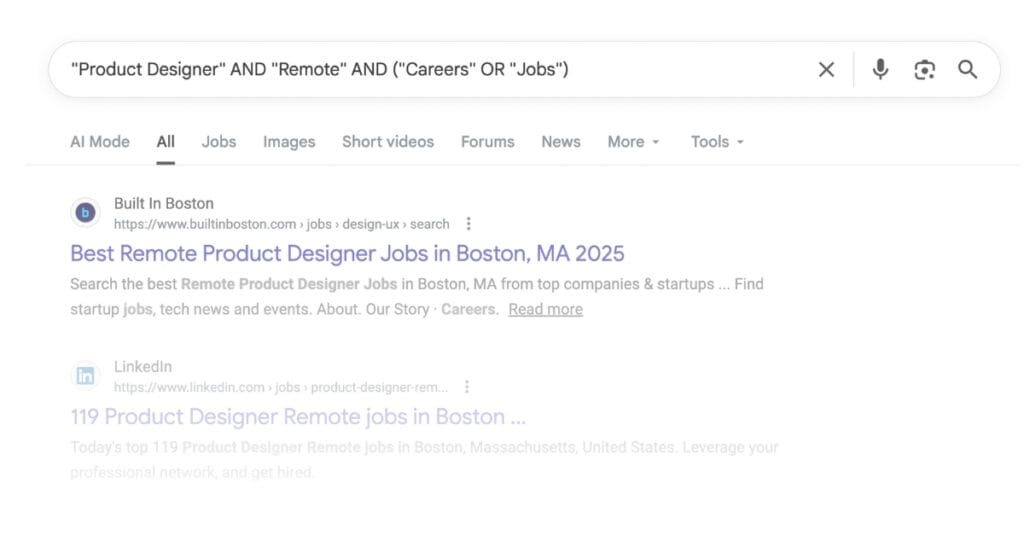
If Boolean search sounds intimidating, do not overthink it. This is just candidates MacGyvering the search ecosystem to get what they want. The same way you would not search “car” if you needed a Toyota Camry with specific features in a specific city, candidates are not typing vague queries and hoping for the best.
They are searching with intent. Your job description either matches that intent or disappears.
When writing a job description for traditional search, focus on three things:
1. Keyword matching
Include the job title, location, and relevant skills clearly and deliberately. Put yourself in the candidate’s shoes and ask what they would actually type into Google. Better yet, ask the hiring manager or incorporate <job target data>. Guessing is how job descriptions get buried.
2. Structured data
Think of Structured Data as the envelope that tells Google what’s inside the letter. Without a JobPosting schema, Google has to “guess” your salary range or location. With it, you get that coveted “Google Jobs” box at the top of the search results. Most modern ATS systems do this automatically, but if yours doesn’t, you are essentially invisible to 70% of the market.
3. Content clarity over clever language
You don’t need to make your job description an ad campaign. You can show personality without being cryptic. If a human or a machine has to work too hard to understand the role, you have already lost.
How can I optimize job descriptions for LinkedIn and job platforms?
Recruiting platforms and social networks run on their own built-in algorithms and engagement loops. Visibility here depends on how your job description is categorized and how candidates interact with it.
When writing a job description for LinkedIn, Indeed, ZipRecruiter, and similar platforms, focus on:
1. Title normalization
No one is searching for “Growth Ninja,” I promise! Use a standard, recognizable title that aligns with how candidates search and how platforms index roles.
2. Skill matching
Skills are not filler. Platforms use them to decide who sees your job. Be specific, be accurate, and resist the urge to pad the list.
3. Engagement signals
Clicks, applies, and shares influence distribution. If you have a budget to promote your job ad, that helps. If you don’t, no worries… tap into your organization to share your LinkedIn job posting. Ensure the first line of the job ad or shared post is attention-grabbing and includes the key info (title, location) because on LinkedIn feeds, only the first snippet may show.
How can I optimize job descriptions for LLMs (ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini)?
We treat ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini like they’re sentient recruiters. The reality? They aren’t clever; they’re just hyper-efficient filters.
Here is the shift you need to make: LLMs don’t rank jobs; they select them. If your JD is a maze of “culture speak” and internal jargon, the model won’t try to solve the puzzle…it will just skip it. When a candidate asks for “Remote Product Marketing roles in SaaS,” the AI isn’t looking for a “vibe.” It’s scanning for data points.
To ensure your roles actually make the cut, optimize for these four pillars:
- Hard Entity Extraction (see below): Clearly define Role, Location, Industry, and Seniority. If you don’t spell it out, the machine won’t guess it.
- The “Plain English” Summary: Write a three-sentence summary that a 5th grader (and an algorithm) can parse instantly.
- Semantic Structure: Use H2 headings and bulleted lists. Clean formatting is the “API” that allows LLMs to ingest your data.
- Data Over Drama: Swap “Rockstar” and “Fast-paced” for specific tools, years of experience, and measurable outcomes. To an LLM, fluff is just white noise.
Example of an Entity Block:
- Role: Senior Product Marketer
- Industry: B2B SaaS / HR Tech
- Seniority: Mid-Senior (5+ years)
- Location: Remote (US-Based)
- Tech Stack: Salesforce, HubSpot, Pendo
You aren’t just writing for humans anymore. You’re writing for the systems that decide if a human ever sees your post. If a machine has to guess what your job is, you’ve already lost the candidate.
💡 Try this Prompt!
Copy and paste your current job description into an LLM with these instructions to “machine-optimize” it:
____
I am going to provide a job description. Please rewrite it to be highly discoverable for LLMs (like ChatGPT and Perplexity).
- Extract Entities: Ensure the job title, industry, seniority level, and location are explicitly stated.
- Increase Signal: Replace vague ‘corporate-speak’ (e.g., ‘rockstar,’ ‘ninja’) with concrete skills and tools.
- Structure: Use clear H2 headings and bulleted lists for responsibilities and requirements.
- Summary: Add a 3-sentence ‘Plain English’ summary at the very top.
[Paste a JD at the end]
____
The New Rule: How to Write Job Descriptions for Humans and Machines
I know it can feel daunting to write job descriptions for humans and machines at the same time. They all operate differently, right?
Take a breath. I’ve got you.
Before you write your next job description, keep these three truths in mind:
- Humans skim
- Platforms Match
- LLMs Summarize
That’s it. That’s the framework.

This mantra works because there is more overlap between human behavior and machine behavior than most people realize. And that overlap is solvable with a handful of smart, repeatable techniques.
Start with your SEO fundamentals and build from there. Below is a short list that covers both human skimming and LLM visibility without turning your job description into a science experiment. If you’re going to save something from this article, save this list:
- Use the job title as your primary keyword
- Standardized job titles beat creative ones. They are clearer for humans and easier for machines to interpret
- State the job title, company, location, and role purpose at the very top
- Lead with skills. Skills-first language improves matching across platforms
- Include salary and benefits. Transparency increases reach and engagement
- Maintain JobPosting structured data and accurate meta information on the page
- Use plain language. LLMs read it cleanly, and implicit jargon confuses machines
- Early engagement matters. Strong early clicks and applies can unlock broader distribution on platforms like LinkedIn
- Align on job benchmarks with the hiring manager early, not after the role is live
You do not need to outsmart the algorithms. You just need to stop making them work so hard. Clear titles, real skills, plain language. Turns out that helps humans too.
Job Benchmarks that match how the market actually searches
Did you know that you can use your job description to stand out to specific types of candidates and still show up in search engines? There’s a balance. This is where we’ve seen our clients use PI data to show up.
Our Job Benchmarks are built from millions of assessments across real people in real roles. That means they reflect:
- How jobs are actually performed
- How roles differ by level, function, and context
- Patterns that repeat across industries and geographies
This enables job descriptions to:
- Use market-validated role language instead of internal jargon
- Match the behavioral and functional expectations candidates recognize
- Avoid over- or under-scoping roles, which is a major driver of low applicant quality
From a discoverability standpoint, this matters because:
- Search engines favor job descriptions that resemble canonical versions of a role
- Higher relevance leads to better engagement, which leads to better rankings
- Candidates self-select more accurately when a role “sounds right”
Why This Matters More for High-Volume and Hard-to-Fill Roles
When talent supply is tight, discoverability becomes a competitive advantage.
When supply is abundant, clarity and relevance matters more than ever.
In both of the above scenarios, job descriptions have an outsized impact. That impact is most visible in high-volume and hard-to-fill roles, where hiring mistakes are expensive, slow to fix, and immediately felt by the business.
In these environments, vague job descriptions do not just slow hiring. They increase risk.
Here are some role-specific recommendations for you:
Optimizing for machines is the first step, but the final goal is attracting the right human. The more operationally critical the job, the less room there is for “creative” writing.
Here is how to apply high-clarity standards across specific functions:
- Sales: Filter for the “Motion” A strong JD filters for sellers who can win in your specific environment. Don’t just list “sales experience.” Use clear language around deal complexity, buyer personas, and cycle lengths. This surfaces candidates who can actually close, not just those who can talk.
- Operations: Kill the Ambiguity In operations, ambiguity creates drag. Move away from vague “support” language and define ownership, scope, and outcomes upfront. This helps you hire architects who improve systems, rather than task-runners who just manage the status quo.
- Frontline & Hourly: Accuracy Over Everything For frontline roles, transparency is your best retention tool. Be explicit about schedules, physical pace, and working conditions. Setting accurate expectations early reduces “Day 1” attrition and lowers the massive cost of constant rehiring.
- Healthcare: Precision as a Safety Metric In clinical environments, job descriptions must reflect clinical demands, compliance requirements, and emotional load. When expectations are blurry, burnout spikes and patient care is put at risk. Clarity here is a matter of safety.
- Manufacturing: Consistency and Discipline Manufacturing roles require a specific temperament. Use your JD to highlight safety standards, quality requirements, and technical tolerances. This attracts candidates who respect the process and reduces the risk of costly errors on the floor.
- Logistics: Coordination Under Pressure Logistics environments run on time. Your JD should target the ability to prioritize and adapt without disrupting the chain. Misalignment in logistics shows up fast; clear writing ensures your new hire can hit the ground running.
Across every one of these roles, the pattern is the same. Vague writing leads to bad hires. The more critical the role, the more you need a “Machine-Ready” JD that leaves zero room for interpretation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why don’t creative job titles perform well in search?
Creative titles like “Growth Ninja” or “Sales Rockstar” fail because they don’t match search intent. Search engines and job boards rely on “Title Normalization” to categorize roles. If your title doesn’t match the standard language used by candidates, your posting becomes invisible to the algorithms that index and surface opportunities.
How do candidates actually discover jobs today?
Job discovery has shifted to a three-channel ecosystem:
- Search Engines: Like Google and Bing.
- Job Platforms/Social Networks: Like LinkedIn and Indeed.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): Like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Gemini.
Because systems filter these jobs long before a human recruiter or candidate interacts with them, machine-readability is now a prerequisite for visibility.
What does it mean to optimize a job description for SEO?
SEO optimization for JDs involves aligning content with how humans actually type queries. This includes using standardized job titles, explicitly listing required skills, stating clear location details, and—most importantly—implementing JobPosting structured data so search engines can correctly index the role in dedicated job search features like Google for Jobs.
How are job platforms like LinkedIn different from search engines?
While search engines focus on keywords and intent, platforms like LinkedIn use engagement algorithms. Visibility depends on how well the role is categorized by skills and how quickly candidates click or apply. High-quality “early signals” (like shares from your employees) tell the platform your role is relevant, triggering wider distribution in candidate feeds.
How do LLMs like ChatGPT and Perplexity surface job opportunities?
Unlike traditional search engines that rank by link authority, LLMs select by entity matching. They scan your text for specific facts—role, location, seniority, and industry. If an LLM cannot easily extract these data points because they are buried in “culture speak,” it will exclude your role from its summary to the candidate.
What makes a job description “LLM-friendly”?
An LLM-friendly JD prioritizes structure over style. This means using a “Plain English” summary at the top, clear headings for different sections, and bulleted lists for skills and requirements. Plain language is easier for a model to “tokenize” and summarize than flowery, metaphorical prose.
Why do job benchmarks matter for discoverability?
Market-validated benchmarks, like those from The Predictive Index, provide a “canonical” version of a role. When your JD aligns with these industry-standard behavioral and functional patterns, search engines and AI models recognize the role as high-relevance, which improves your ranking and ensures you attract candidates who actually fit the work.
Why does clarity matter more for high-volume or hard-to-fill roles?
In high-stakes hiring, ambiguity is a massive financial risk. For high-volume roles, vague JDs lead to poor self-selection, which spikes attrition and rehiring costs. For hard-to-fill roles, clarity acts as a trust signal for top-tier talent; the best candidates want to know exactly what the “win” looks like before they ever hit “apply.”